
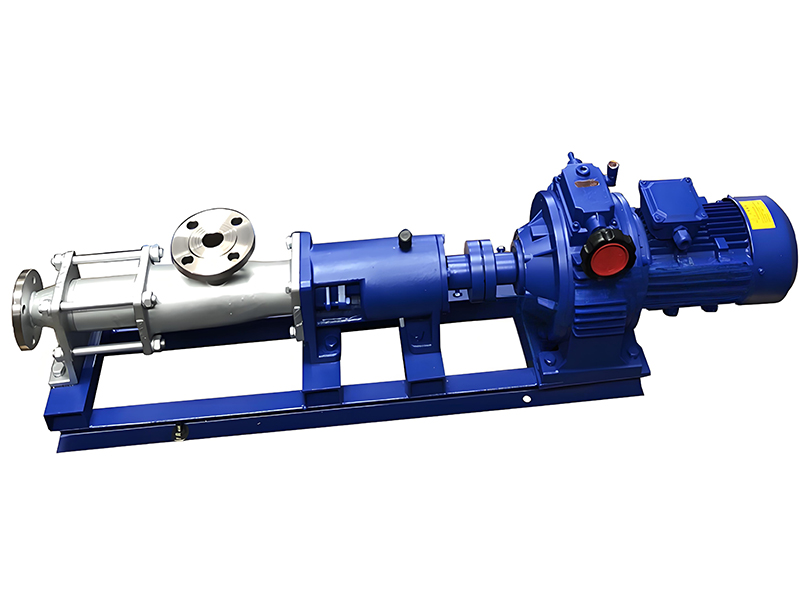
The G-type horizontal single-screw pump, also known as a horizontal Progressive cavity pump, is a high-performance positive displacement pump designed for continuous and stable fluid transfer. It is especially suitable for handling viscous, abrasive, or shear-sensitive fluids in industrial environments. The pump operates on the principle of a progressive cavity, where a single helical rotor rotates inside a double-helical stator, forming sealed cavities that move the medium from the suction end to the discharge end smoothly and without pulsation.
Compared to traditional centrifugal pumps, the G-type horizontal single-screw pump offers steady flow without agitation or pulsation, ensuring minimal shear and maintaining the integrity of transported materials. This makes it ideal for applications involving sludge, slurry, oil, sewage, glue, resins, polymers, and food pastes. The horizontal layout provides a compact footprint, convenient installation, and easy maintenance.
The rotor and stator form the core components of the G-Type Screw Pump. The rotor is typically made of high-strength stainless steel (304 or 316L) and precision-machined to achieve excellent wear resistance and corrosion protection. The stator is composed of special elastomer materials such as NBR, EPDM, or FKM, chosen according to the chemical properties and temperature of the conveyed medium. This combination ensures superior sealing, long service life, and efficient performance even under harsh conditions.
The horizontal design offers additional advantages in terms of stability and accessibility. It allows for direct coupling with electric motors, gear reducers, or variable frequency drives (VFDs) to achieve speed control and flow adjustment. The G-type horizontal single-screw pump is widely adopted in industrial wastewater treatment, petrochemical industries, food processing, mining, and power plants, meeting the requirements of continuous heavy-duty operations.
The pump’s self-priming ability enables it to handle fluids with entrained air or gas content, while its bidirectional rotation feature allows for both forward and reverse flow. These properties make it versatile for various fluid transfer systems, from simple feed operations to complex dosing and mixing applications. The pump’s modular structure also simplifies disassembly, inspection, and maintenance, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the G-type horizontal screw pump offers customizable configurations. Depending on the customer’s needs, the pump can be equipped with:
Mechanical seals or packing seals for different fluid sealing requirements
Explosion-proof motors for hazardous environments
Stainless steel housings for corrosive or hygienic applications
Heating jackets or cooling systems for temperature-sensitive materials
With its combination of reliability, durability, and precision, the G-type horizontal single-screw pump has become a preferred solution for industries demanding consistent and efficient fluid transfer.
The performance of the G-type horizontal single-screw pump depends on several parameters, which can be customized to meet the user’s process requirements. The following are typical specifications and configurations found in industrial models.
| Parameter | Specification Range |
Flow Rate (Q) | 0.1 to 150 m3/h |
Discharge Pressure (P) | Up to 1.2 MPa (12 bar) |
Suction Lift | Up to 8 meters |
Temperature Range | -20°C to +120°C (depending on stator material) |
Viscosity Range | Up to 1,000,000 cP |
Solid Content | ≤ 40% (depending on particle size) |
Rotor Material | Stainless Steel 304 / 316L / Duplex Steel |
Stator Material | NBR, EPDM, FKM, or customized elastomers |
Pump Casing Material | Cast Iron / Stainless Steel / Carbon Steel |
Drive Type | Direct-coupled, gear motor, or belt-driven |
Seal Type | Mechanical seal or packing gland |
Motor Power | 0.75 – 22 kW (customizable) |
Installation Type | Horizontal base-mounted |
Connection Type | Flanged / Threaded / Clamp-type |
The G-type screw pump’s flow rate and pressure are linearly proportional to its rotational speed, allowing for precise control of output through a frequency converter. This is a key advantage in dosing, metering, and variable flow applications.
Its modular construction ensures that components such as rotors, stators, couplings, and shafts can be replaced individually, simplifying maintenance and lowering life-cycle costs. The pump can also be fitted with pressure relief valves, dry-run protection, and monitoring sensors to ensure safe and reliable operation.
The mechanical seal options vary based on media type — for example, single mechanical seals are standard for clean fluids, while double mechanical seals are recommended for abrasive or hazardous liquids. For high-viscosity materials or media with suspended solids, hardened rotors and wear-resistant stators are preferred.
All pumps undergo hydraulic testing and performance calibration before delivery to ensure compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, CE, and API 676 for progressive cavity pumps.
The G-type horizontal single-screw pump is highly versatile, making it suitable for a wide range of industries that require stable, low-pulsation flow for liquids with different viscosities and solid content. Its adaptability, reliability, and simple maintenance design make it a core component in industrial fluid handling systems across multiple sectors.
In wastewater treatment plants, the G-type horizontal single-screw pump is used for sludge transfer, dewatered cake transport, polymer dosing, and thick slurry conveyance. It efficiently handles viscous and solid-laden fluids without clogging. The pump’s gentle conveying motion prevents floc breakdown, maintaining polymer effectiveness and treatment quality. It is often installed in sludge dewatering systems, clarifier feed lines, and dosing stations.
In the chemical industry, the pump is essential for handling acids, alkalis, resins, solvents, emulsions, adhesives, and oil derivatives. The availability of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel 316L and FKM elastomers allows the pump to operate safely in chemically aggressive environments. In petrochemical plants, it is used to transfer crude oil, bitumen, lubricants, and polymer solutions, ensuring accurate flow rates for continuous processes.
The G-type single-screw pump’s low shear and gentle conveying action make it ideal for the food sector. It is widely used for pumping viscous products such as honey, syrup, chocolate, jam, yogurt, and sauces. When equipped with food-grade stainless steel components and sanitary mechanical seals, it complies with FDA and hygienic standards, preventing contamination and maintaining product texture. The horizontal design allows for easy cleaning and integration with CIP (Clean-In-Place) systems.
In mining operations, the G-type pump is used to convey mineral slurries, tailings, and abrasive mixtures. Its strong suction and ability to handle high-solid-content fluids make it a reliable choice for continuous operation under harsh conditions. The wear-resistant design, combined with hardened rotor materials, ensures durability even in applications involving sand, coal slurry, or metal concentrates.
In the oil and energy sectors, the pump is applied for crude oil transfer, oil-water separation systems, fuel delivery, and drilling mud circulation. Its robust design and explosion-proof motor options ensure safe operation in potentially hazardous environments. Additionally, the pump is compatible with biogas and biomass slurry feeding systems, supporting renewable energy production.
The G-type horizontal screw pump is also used in cement, gypsum, and ceramic slurry transport, as well as in concrete additives and polymer mortar production. Its ability to handle thick, non-flowing materials makes it suitable for continuous dosing and transfer in construction applications.
Across all these industries, the G-type screw pump demonstrates consistent performance, high reliability, and low operational cost — making it a trusted solution for engineers and plant managers seeking long-term efficiency.
To ensure optimal performance and extend the service life of the pump, proper installation, operation, and maintenance procedures must be followed. Below are comprehensive guidelines for using the G-type horizontal single-screw pump safely and efficiently.
Before installation, ensure that the foundation is level and vibration-free. The pump and motor should be mounted on a rigid base frame. The suction and discharge pipelines must be aligned with the pump ports to prevent stress on the casing. Flexible couplings should be used between the motor and pump shaft to compensate for minor misalignment. The inlet pipe should be as short and straight as possible to reduce suction losses.
Always check the rotation direction before starting the pump. Incorrect rotation can cause stator damage or seal failure. Ensure that the pump is fully primed with liquid before startup to avoid dry-running, which can severely damage the stator.
Before starting:
Fill the pump cavity with liquid to lubricate the stator.
Confirm that suction and discharge valves are open.
Ensure that all electrical connections are secure and the motor is properly grounded.
Start the motor and allow it to reach the rated speed gradually. Monitor the discharge pressure, flow rate, and power consumption to ensure they are within design limits. The pump can operate in both directions, but the standard direction is clockwise when viewed from the drive end.
If the pump is equipped with a frequency converter, adjust the speed to control flow precisely. Do not exceed the maximum rated pressure or torque, as it may lead to mechanical stress or seal leakage.
Routine inspection and maintenance are critical to ensuring long-term reliability:
Lubricate bearings regularly according to the manufacturer’s recommendation.
Inspect the mechanical seal or packing gland for leakage and adjust or replace as needed.
Check the rotor and stator periodically for signs of wear, deformation, or corrosion.
Clean the suction strainer and pipelines to prevent clogging.
If the pump is idle for a long period, drain the liquid, clean internal surfaces, and apply protective grease to prevent corrosion. For high-viscosity or temperature-sensitive media, flush the system with a compatible solvent after use.
Never operate the pump without liquid in the suction chamber.
Avoid running the pump against a closed discharge valve.
Monitor temperature rise in bearings and stator during continuous operation.
When transferring flammable liquids, ensure that the pump is grounded and explosion-proof.
For abrasive media, use hardened rotors and wear-resistant stators to extend lifespan.
Proper operation not only prevents premature wear but also ensures maximum energy efficiency and process stability.
Although the G-type horizontal single-screw pump is known for its reliability and durability, proper maintenance and operation are essential for preventing downtime. The following FAQ section outlines common problems, their possible causes, and practical solutions to keep your system running efficiently.
Possible Causes:
Pump not properly primed (air trapped inside)
Incorrect rotation direction
Suction valve closed or blocked
High suction lift exceeding design limit
Solutions:
Fill the suction chamber with fluid and vent trapped air.
Verify motor rotation direction before startup.
Open suction and discharge valves fully.
Reduce suction height or check for leaks in suction piping.
If the pump remains unresponsive, inspect the mechanical seal and coupling alignment, as misalignment may cause the rotor to jam inside the stator.
Possible Causes:
Rotor or stator wear due to prolonged use
Air or gas leakage into the suction line
Blockage or scaling in the discharge pipe
Operating speed too low
Solutions:
Replace worn rotor and stator elements.
Tighten suction connections and inspect seals.
Clean suction and discharge lines.
Adjust motor speed or frequency converter to design RPM.
A gradual decline in flow usually indicates stator wear, especially when handling abrasive media such as sand or sludge. Regular inspection intervals are recommended to maintain optimal efficiency.
Possible Causes:
Excessive pressure or temperature
Worn or damaged seal faces
Improper seal installation or misalignment
Dry-running during startup
Solutions:
Check pressure and temperature against rated limits.
Replace seals or packing with compatible materials.
Ensure lubrication of seal faces with pumped fluid.
Install dry-run protection sensors for automatic shutdown.
In corrosive environments, always select 316L stainless steel components and chemical-resistant seal materials such as PTFE or FKM to ensure long-term sealing reliability.
Possible Causes:
Misalignment between motor and pump shaft
Air cavitation in suction line
Loose foundation bolts or flexible coupling
Bearing wear or rotor imbalance
Solutions:
Realign the coupling and ensure proper motor-pump alignment.
Check for air leaks and maintain positive suction pressure.
Tighten mounting bolts and replace worn bearings.
Verify that the pump is not running above rated speed.
Cavitation should be addressed immediately, as it can cause erosion and premature rotor failure.
Possible Causes:
Excessive discharge pressure or blocked outlet
High viscosity beyond rated capacity
Stator swelling due to chemical incompatibility
Bearing friction or misalignment
Solutions:
Check discharge line and relieve pressure.
Reduce flow or use a speed controller to adjust load.
Replace stator with appropriate elastomer (NBR, EPDM, or FKM).
Inspect bearings and lubricate as required.
To optimize energy efficiency, select a motor with suitable torque margin and use variable frequency drives (VFD) for controlled operation under varying loads.
Possible Causes:
Dry-running or insufficient lubrication
High solid content or abrasive particles
Chemical incompatibility between stator and fluid
Excessive operating temperature
Solutions:
Ensure liquid is present before startup.
Install filters or strainers on suction side.
Choose stator material compatible with fluid chemistry.
Monitor temperature and prevent overheating.
Regular monitoring of pump pressure, vibration, and flow performance helps detect wear early and prevents unexpected shutdowns.
To extend the service life of your G-type horizontal single-screw pump, follow these maintenance best practices:
Conduct a monthly inspection of seals, bearings, and couplings.
Replace worn stators and rotors at the first sign of performance decline.
Keep accurate records of operation hours and maintenance intervals.
Use only OEM spare parts to ensure dimensional compatibility.
Calibrate motor controls and sensors regularly.
When properly maintained, a G-type screw pump can operate continuously for 10,000–15,000 hours with minimal downtime — making it one of the most cost-effective solutions for industrial fluid handling.

Copyright ? Jiangsu Longjie Pump Manufacturing Co., Ltd.